In this post I am going to cover the mystery of omega 3 fatty acids and the benefits of omega 3 in bodybuilding.
What is omega 3 fatty acid?
Omega-3 fatty acids are a type of polyunsaturated fat that are essential for good health. They play a crucial role in brain function, growth, and development. There are two main classes of polyunsaturated fatty acids, PUFA’s. Omega 3 and Omega 6.
Omega 3 is present in foods such as flaxseed, fish and supplements like fish oil.
Most common omega 3 are ALA, EPA, DHA.
ALA is an essential fatty acid, meaning the body cannot produce it. It must be obtained from diet.
Ala can be converted to EPA, DHA but the conversion happens in the liver and the rate of conversion is very low.
Therefore the only way to obtain EPA and DHA is via diet or supplements.
ALA is present in plants like flaxseed, soybean, canola oil.
DHA & EPA are present in fish oils, krill oil. The actual source of omega 3 is microalgae. When fish consume phytoplankton that consume microalgae, they accumulate omega-3s in their tissues.
Types of omega 3 fatty acids
There are three main types of omega-3 fatty acids:
ALA (alpha-linolenic acid)
This is found in plant oils such as flaxseed, soybean, and canola oils, as well as in walnuts and leafy vegetables. ALA is converted into EPA and DHA in the body, but this conversion is not very efficient.
EPA (eicosapentaenoic acid):
This is found mainly in fish, particularly fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, and sardines. EPA is important for reducing inflammation and improving heart health.
DHA (docosahexaenoic acid):
Like EPA, DHA is found in fatty fish and is important for brain function and eye health. It is a major structural component of the brain and the retina of the eye.
Our body doesn’t produce omega-3s on its own, so you need to get them from your diet or supplements.
Functions of omega 3 fatty acids
- They are the components of phospholipids that form structure of cell membrane
- DHA is especially high in retina, brain and sperm.
- The provide energy to the body and are used to form eicosanoids
- Eicosanoids have wide functions in cardiovascular, pulmonary, immune and endocrine systems
Ratio of omega 3 to omega 6
Some researchers believe that the ratio of omega 3 to omega 6 may have important implications for pathogenesis of diseases such as CVD and cancer.
But the optimal ratio has not been defined and it is better to have a higher level of EPA and DHA in blood.
Recommended omega 3 dosage
You should aim for 2000 to 3000 mg of EPA and DHA everyday. This dose should help you with faster muscle recovery, lower inflammation and improved immune functions.
Sources of omega 3
Omega 3 is mostly available in fish. However the omega 3 content varies for different types of fish.
Cold water fatty fish like salmon, mackerel, tuna, sardines have high amounts of omega 3 fatty acid.
Fish with lower fat content like basa, tilapia, cod have lower omega 3 content.
Beef is very low in omega 3.
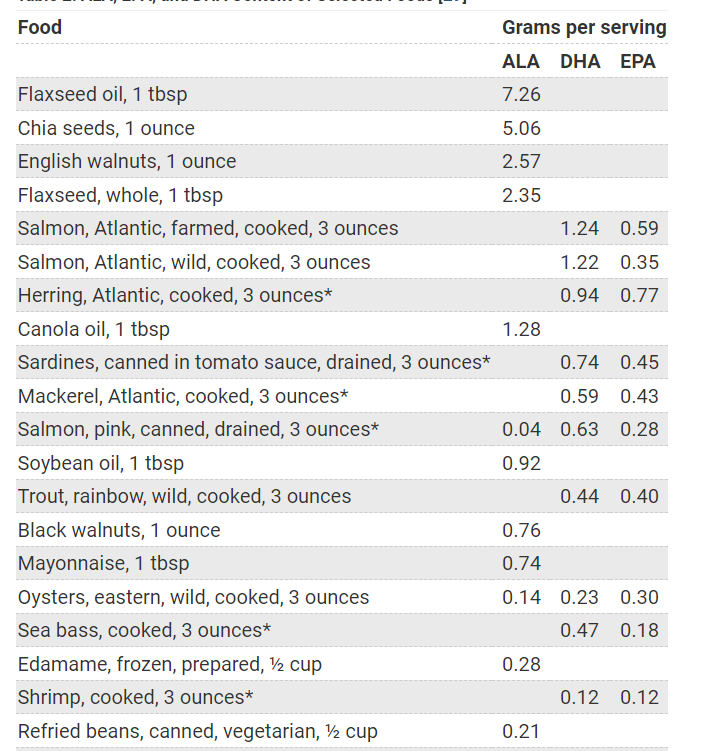
Source : https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/
Omega 3 supplements
Omega 3 supplements are present in various forms such as fish oil, krill oil, cod liver oil and plant based products like algal oil.
A typical fish oil supplement may contain 180 mg EPA and 120 mg DHA. but doses vary.
Supplements have different forms of fish oil
- Natural triglycerides
- Free fatty acids
- Ethyl esters
- Re-esterified triglycerides and
- Phospholipids
Omega 3 deficiency
Deficiency of omega 3 can lead to a lot of issues like dry skin, brittle hair, joint pain, poor immune functions, poor brain functions
Omega 3 bodybuilding benefits
Omega-3s are polyunsaturated fats vital for cell membranes, energy production, and overall cellular function. They help lower triglycerides, support cardiovascular health, and may reduce the risk of certain diseases.
Anti inflammatory effects
Omega 3 fatty acids reduce inflammation. Intense workouts can cause inflammation in the body and omega 3 fatty can help
Joint benefits
Bodybuilders often train hard and joint pain is common. Omega 3 fatty acids improve joint mobility and flexibility. They prevent the breakdown of cartilages. They also help in maintaining the synovial fluid that lubricates the joint.
Muscle protein synthesis
While the research is not conclusive here are few things that help
- Anabolic signaling – some research indicates the omega 3s may activate mTor pathway. This regulates muscle protein synthesis
- Muscle recovery – omega 3’s help with faster recovery. Which means you train harder and with higher frequency.
- Gene expression – omega 3 can influence genes involved in lipid metabolism, glucose metabolism, and inflammatory response.
Omega 3 and body composition
Omega helps with appetite regulation, they also help with faster recovery. Omega 3s influence hormone levels for insulin, leptin, and adiponectin. Thus omega 3 can have a positive impact on body composition
Omega 3 and Cardiovascular health
Researchers have found the consumption of fatty fish and higher plasma level of omega 3 is associated with lower risk of heart diseases such as heart failure, coronary disease.
When to take fish oil for bodybuilding
When taking a fish oil supplement we have to keep a few things in mind. If you have trouble with consistency, you can fix a set time for example early or just before our workout or after workout.
If you notice burps with fish oil you can try taking them with meals.
There are some studies that suggest that fish oil helps with inflammation so you can try taking your supplement before or after your workouts
Omega 3 bodybuilding Faq
Q How much EPA and DHA per day for bodybuilding?
A study of 5 week 1600 mg EPA and 800 mg DHA consumption has reported bodybuilding benefits like supporting cognitive functions, neuroprotective effects and recovery time.
In general we can take up to 3 gms of EPA and DHA, this is considered as safe dosage.
Omega 3 for bodybuilding summary
Overall omega 3 is widely studied and researched. Omega 3 is known for its anti-inflammatory benefits, it helps in muscle protein synthesis, improves body composition and helps in heart health. If you are lifting weights regularly you should consider supplementing omega 3 or increase fish consumption in your diet.
References
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7761957/
https://nutrition.org/does-omega-3-fatty-acid-supplementation-help-you-build-muscle/
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3737804/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0195666308004972
https://ods.od.nih.gov/factsheets/Omega3FattyAcids-HealthProfessional/
https://nutritionj.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1475-2891-9-10

